الگوی جامع عوامل اثرگذار بر شکست حسابرسی: رویکرد مبتنی بر رگرسیون لوجیت
کلمات کلیدی:
شکست حسابرسی, خطای حسابرسی, اظهارنظر حسابرسیچکیده
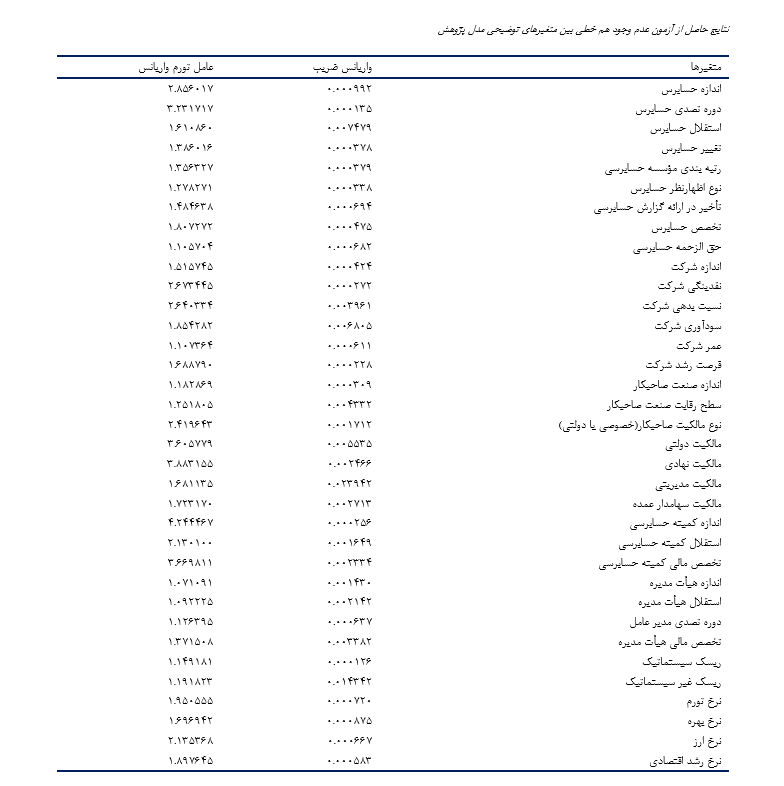
هدف پژوهش حاضر تبیین عوامل مؤثر (شامل ویژگیهای حسابرس، ویژگیهای صاحبکار، ویژگیهای بازار سهام و اقتصاد کلان) بر شکست در شرکتهای پذیرفته شده در بورس اوراق بهادار تهران میباشد. به منظور نیل به این هدف 1848 سال-شرکت (154 شرکت برای 12 سال) مشاهده جمع آوری شده از گزارشهای مالی سالیانه شرکتهای پذیرفته شده در بورس اوراق بهادار تهران در طی دوره زمانی 1390 تا 1401 مورد آزمون قرار گرفتهاند. یافتههای پژوهش نشان میدهد که اندازه حسابرس، دوره تصدی حسابرس، استقلال حسابرس، رتبه بندی مؤسسه حسابرسی، نوع اظهارنظر حسابرس، تأخیر در ارائه گزارش حسابرسی، تخصص حسابرس، حق الزحمه حسابرسی، اندازه شرکت، نقدینگی شرکت، سودآوری شرکت، مالکیت نهادی، مالکیت سهامدار عمده، استقلال هیأت مدیره، دوره تصدی مدیر عامل، نرخ تورم، نرخ ارز و نرخ رشد اقتصادی بر شکست حسابرسی تأثیر منفی و معناداری دارند. در حالی که، تغییر حسابرس، نسبت بدهی شرکت، مالکیت دولتی، ریسک غیر سیستماتیک و نرخ بهره بر شکست حسابرسی تأثیر مثبت و معناداری دارند. در نهایت نتایج پژوهش نشان میدهد که از لحاظ آماری، عمر شرکت، فرصت رشد شرکت، اندازه صنعت صاحبکار، سطح رقابت صنعت صاحبکار، نوع مالکیت صاحبکار(خصوصی یا دولتی)، مالکیت مدیریتی، اندازه کمیته حسابرسی، استقلال کمیته حسابرسی، تخصص مالی کمیته حسابرسی، اندازه هیأت مدیره، تخصص مالی هیأت مدیره حسابرس و ریسک سیستماتیک تأثیر معناداری ندارند.
دانلودها
مراجع
Aggreh, M., Malgwi, C. A., & Enyi-Igbokwe, A. E. (2018). Does Adoption of International Financial Reporting
Standards (IFRS) Affect Financial Performance? Evidence From Nigerian Deposit Money Banks. International
Journal of Accounting and Financial Reporting, 8(3), 51. https://doi.org/10.5296/ijafr.v8i3.13309
Bebbington, J., & Larrinaga, C. (2024). The influence of Power’s audit society in environmental and sustainability
accounting. Qualitative Research in Accounting & Management, 21(1), 21-28. https://doi.org/10.1108/QRAM-01-
-0007
Chang, C., Chi, W., & Liu, C. (2003). Client Characteristics and Auditor Switch in an Audit Failure.
Chu, L., Fogel-Yaari, H., & Zhang, P. (2024). The Estimated Propensity to Issue Going Concern Audit Reports and Audit
Quality. Journal of Accounting, Auditing & Finance, 39(2). https://doi.org/10.1177/0148558X221079011
De Fuentes, C., & Porcuna, R. (2019). Predicting audit failure: evidence from auditing enforcement releases. Spanish
Journal of Finance and Accounting, 48(3), 274-305. https://doi.org/10.1080/02102412.2018.1524220
Francis, J. R. (2011). A framework for understanding and researching audit quality. Auditing: A Journal of Practice &
Theory, 30(2), 125-152. https://doi.org/10.2308/ajpt-50006
Hamidian, M., & Seifi, G. (2022). The Relationship Between Product Diversification and Audit Errors in Tehran Stock
Exchange. Accounting and Management Perspective, 5(69), 100-115.
https://www.jamv.ir/article_163898.html?lang=en
Hassani, M. (2021). Evaluating the Relationships Among the Risk of Undetected Errors Due to Audit Error Probability,
Competitive Market Environment of Audit Services, and Audit Service Pricing. Accounting Knowledge Journal,
(1), 45-68. https://www.sid.ir/paper/399235/en
Hassas Yeganeh, Y., & Azinfar, K. (2010). The Relationship Between Audit Quality and Audit Firm Size. Accounting
and Auditing Reviews(61), 85-98. https://acctgrev.ut.ac.ir/article_21687.html
Hemmati, A., Hejazi, R., & Sedaghat Parast, E. (2020). The Impact of Information Complexity on Audit Failures in
Corporate Fraud (Tehran Stock Exchange). Professional Auditing Research Quarterly, 1(1), 34-55.
Kabir, H., Su, L., & Rahman, A. (2016). Audit failure of New Zealand finance companies-an exploratory investigation.
Pacific Accounting Review, 28(3), 279-305. https://doi.org/10.1108/PAR-10-2015-0043
Muraina, A., Okpara, E., & Ahunanya, S. (2010). Transparency in corporate governance; A comparative study of
ENRON, USA and Cadbury PLC, Nigeria. Medwell Journals, 5(6), 471-476.
https://doi.org/10.3923/sscience.2010.471.476
Osho, A., Olutayo, M. E., & Olayinka, E. A. (2021). International financial reporting standards (IFRS) and financial
performance of multinational companies in Nigeria. The Journal of Accounting and Management, 11(2).
Palmrose, Z. V. (1988). An analysis of auditor litigation and audit service quality. Accounting review, 55-73.
https://www.jstor.org/stable/247679
Xie, F. (2021). Analysis of Measures of Audit Failure. Journal of Forensic and Investigative Accounting, 13(2).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2021.105550
Yuan, H., Zhang, C., Kong, D., & Shi, H. (2019). The consequence of audit failure on audit firms: evidence from IPO
approval in China. China Journal of Accounting Studies, 7(2), 245-269.
دانلود
چاپ شده
ارسال
بازنگری
پذیرش
شماره
نوع مقاله
مجوز
حق نشر 2025 تکنولوژی در کارآفرینی و مدیریت استراتژیک

این پروژه تحت مجوز بین المللی Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 می باشد.










