Designing an Efficient Administrative System Model with a Jihadi Management and Organizational Justice Approach (Case Study: Social Security Organization)
Keywords:
Model design, Efficient administrative system, Jihadi management approach, Organizational justice approach, Social Security OrganizationAbstract
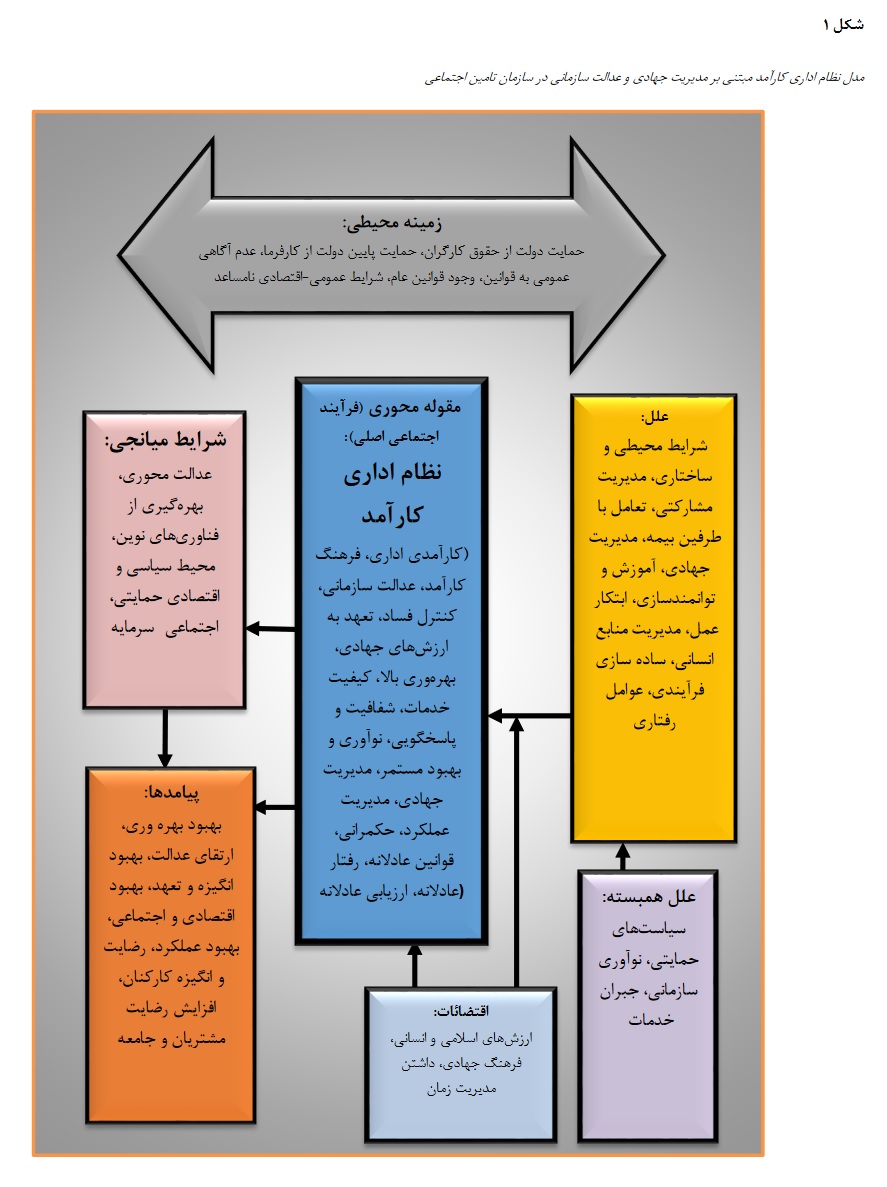
The Social Security Organization, as one of the largest institutions providing social and insurance services in Iran, plays a significant role in ensuring the social and economic security of various segments of society. The objective of this research is to present a model of an efficient administrative system based on justice-oriented and jihadi management principles. This research follows an interpretive philosophy, an inductive approach, a qualitative method, and a grounded theory strategy with an emergent approach. The study population consists of the Social Security Organization, where the qualitative sample includes individuals with at least 10 years of work experience who possess theoretical and practical knowledge related to the research topic and understand the efficient processes of the administrative system within the Social Security Organization. Out of these individuals, 21 were selected as the sample through purposive sampling. To assess the validity of the research, the four criteria of Lincoln and Guba (1987) were used. The findings revealed that 548 initial codes were extracted, categorized into 104 categories and 31 components. For theoretical coding, Glaser's "6 Cs" family was utilized. In this context, the causal components include environmental and structural conditions, participatory management, interaction with insurance parties, jihadi management, training and empowerment, initiative, human resource management, process simplification, and behavioral factors. The correlational factors include supportive policies, organizational innovation, and service compensation. The contingencies involve Islamic and human values, jihadi culture, and time management. The mediating conditions consist of justice-oriented principles, utilization of modern technologies, a supportive political and economic environment, and social capital. The outcomes encompass improved productivity, enhanced justice, increased motivation and commitment, economic and social improvement, better performance, employee satisfaction and motivation, and increased customer and societal satisfaction. Finally, the environmental context includes government support for workers' rights, low government support for employers, public unawareness of laws, the existence of general laws, and unfavorable general-economic conditions.
Downloads
References
Alvarenga, A., Matos, F., Godina, R., & Matias, J. C. O. (2020). Digital transformation and knowledge management in
the public sector. Sustainability (Switzerland), 12(14). https://doi.org/10.3390/su12145824
Azizi, M. (2023). The impact of bureaucracy on the efficiency of social security organizations. Iranian Journal of Public
Administration, 10(2), 78-91. https://doi.org/10.1080/23311975.2023.1215891
Bies, R. J., Moag, J. F., Staw, B. M., & Cummings, L. L. (2021). Interactional justice: Communication criteria of fairness.
In Research in Organizational Behavior (Vol. 9, pp. 289-319). Elsevier.
https://cir.nii.ac.jp/crid/1573387450502494336
Chesbrough, H., & Rosenbloom, R. S. (2017). The role of the business model in capturing value from innovation.
Industrial and Corporate Change, 11(3), 529-555. https://doi.org/10.1093/icc/11.3.529
De Vries, H., Bekkers, V., & Tummers, L. (2016). Innovation in the public sector: A systematic review and future
research agenda. Public Administration, 94(1), 146-166. https://doi.org/10.1111/padm.12209
Farazmand, A. (2021). The role of administrative efficiency in enhancing social security services. Public Organization
Review, 21(4), 765-780. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11115-021-00527-5
Feroz, A. K., Zo, H., & Chiravuri, A. (2021). Digital transformation and environmental sustainability: A review and
research agenda. Sustainability (Switzerland), 13(3), 1-20. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13031530
Ghasemi, R., & Salehi, A. (2023). Human resource challenges in the social security organization of Iran. Journal of
Human Resources management, 15(1), 101-115. https://doi.org/10.1080/23314005.2023.1245875
Ghorbani, M. (2022). Social security and public trust: The influence of administrative efficiency. International Journal
of Social Economics, 49(6), 897-912. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJSE-09-2021-0553
Greenberg, J. (2021). Organizational justice: Yesterday, today, and tomorrow. Journal of Management, 16(2), 399-432.
https://doi.org/10.1177/0149206308330557
Jong, J., & Faerman, S. R. (2023). Centralization and decentralization: balancing organizational and employee
expectations. In Global Encyclopedia of Public Administration, Public Policy, and Governance (pp. 1449-1454).
Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-66252-3_4179
Mohammadi, M., & Tavakoli, N. (2021). Factors influencing administrative efficiency in social security organizations:
A case study of Iran. Journal of Social Security Studies, 8(3), 245-268.
https://doi.org/10.1080/09718923.2021.1885564
Nearchou, F., Hennessy, E., Flinn, C., Niland, R., & Subramaniam, S. S. (2020). Exploring the impact of covid-19 on
mental health outcomes in children and adolescents: A systematic review. International journal of environmental
research and public health, 17(22), 1-19. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17228479
Niehoff, B. P., & Moorman, R. H. (2023). Justice as a mediator of the relationship between methods of monitoring and
organizational citizenship behavior. Academy of Management journal, 36(3), 527-556.
https://doi.org/10.5465/256591
Nikpour, A., & Ebrahimi, S. (2022). Ethical challenges and corruption in Iran's social security system. Journal of Business
Ethics, 176(2), 401-417. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-021-05075-y
Rahimi, A., & Dastjerdi, H. (2020). Corruption and inefficiency in the administrative systems of Iran. International
Journal of Public Administration, 43(11), 944-957. https://doi.org/10.1080/01900692.2020.1713350
Shadmehr, M. (2023). Reforming Iran's social security system: A focus on administrative efficiency. Middle East Journal
of Public Policy, 18(1), 21-36. https://doi.org/10.1080/23344582.2023.1270124
Yeganeh, H., & Amini, M. (2022). Administrative challenges and solutions in the Iranian social security system. Public
Administration Review, 82(4), 123-145. https://doi.org/10.1111/puar.13234
Zhang, J., Long, J., & von Schaewen, A. M. E. (2021). How does digital transformation improve organizational
resilience? - findings from pls-sem and fsqca. Sustainability (Switzerland), 13(20).
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) -1 Journal of Technology in Entrepreneurship and Strategic Management (JTESM)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.










