Analyzing the Role of Informal Learning and Job Insecurity Perception in the Impact of Artificial Intelligence Opportunity Perception on Workplace Well-Being
Keywords:
Artificial intelligence opportunity perception, Employee workplace wellbeing, Informal learning, Job insecurity perceptionAbstract
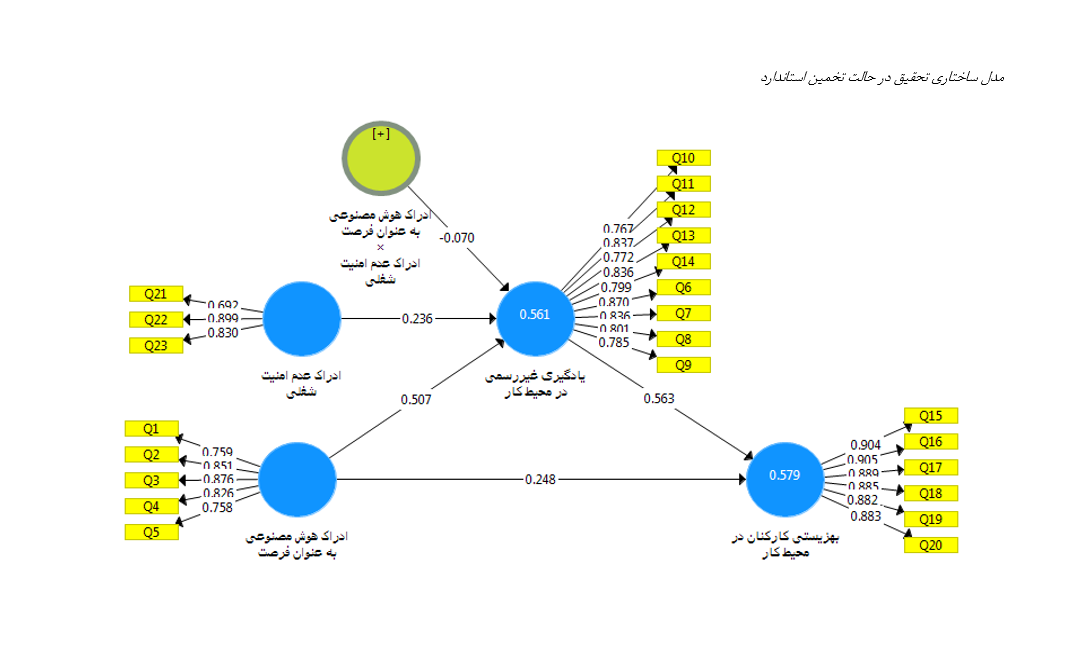
This study investigates the effect of artificial intelligence opportunity perception on employee well-being considering the mediating role of informal learning and the moderating role of job insecurity perception. This applied, descriptive–survey study was conducted among 280 employees of the Iranian Graphic Designers Association in 2025, from which 188 participants were selected using simple random sampling. Data were collected via Xu et al.’s (2023) standardized questionnaire. Structural equation modeling was performed using SmartPLS 3 with descriptive analysis in SPSS 26. AI opportunity perception significantly predicted employee well-being (β=0.248, t=2.459) and informal learning (β=0.507, t=6.080). Informal learning significantly affected well-being (β=0.563, t=6.110). Sobel test confirmed the partial mediating role of informal learning (Z=3.758, p<0.001). Job insecurity perception did not significantly moderate the AI–informal learning relationship (t=1.322). Fostering opportunity-oriented perceptions of artificial intelligence enhances employee well-being primarily through strengthening informal learning processes, regardless of perceived job insecurity.
Downloads
References
Akgunduz, Y., & Eryilmaz, G. (2018). Does turnover intention mediate the effects of job insecurity and co-worker support on social loafing? International Journal of Hospitality Management, 68(4), 41-49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhm.2017.09.010
Aslani, F., & Mohammadi, M. (2025). The Impact of Self-Transcendence on the Well-Being of Isfahan Cemetery Employees: The Mediating Role of Workplace Spirituality and the Moderating Role of Spiritual Leadership. Journal of Religious, Spirituality and Management Studies, 12(24), 151-175. https://rsm.rihu.ac.ir/article_2346.html?lang=en
Cerasoli, C. P., Alliger, G. M., Donsbach, J. S., Mathieu, J. E., Tannenbaum, S. I., & Orvis, K. A. (2018). Antecedents and outcomes of informal learning behaviors: A meta‐analysis. Journal of Business and Psychology, 33(2), 203-230. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10869-017-9492-y
Judijanto, L., Soesanto, D. R., & Pahrijal, R. (2025). Employee Well-Being Research Trends in HR Management. West Science Interdisciplinary Studies, 3(3), 516-527. https://doi.org/10.58812/wsis.v3i03.1781
Karimnzhad, M. H. (2025). Examining the impact of perceiving artificial intelligence as an opportunity on employees' workplace well-being: The role of informal learning and perceived job insecurity (Publication Number Master's thesis in Business Administration (Technology Orientation)) Payame Noor University].
Lu, Y., Papagiannidis, S., & Alamanos, E. (2019). Exploring the emotional antecedents and consequences of technology acceptance. Computers in human Behavior, 90, 153-169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2018.08.056
Martela, F. (2025). Well-Being as Having, Loving, Doing, and Being: An Integrative Organizing Framework for Employee Well-Being. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 46, 641-661. https://doi.org/10.1002/job.2862
Noe, R. A., Clarke, A. D. M., & Klein, H. J. (2014). Learning in the twenty‐first‐century workplace. Annual Review of Organizational Psychology and Organizational Behavior, 1, 245-275. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-orgpsych-031413-091321
Pienaar, J., De Witte, H., Hellgren, J., & Sverke, M. (2013). The cognitive/affective distinction of job insecurity: Validation and differential relations. Southern African Business Review, 17(2), 1-22. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/257749177_The_cognitiveaffective_distinction_of_job_insecurity_Validation_and_differential_relations
Rahmati, M., & Cheriani Zanjani, Y. (2024). Proposing a model to understand how artificial intelligence influences employees' organizational behavior. 8th International Conference on Management and Industry, Tehran, Iran.
Raisch, S., & Krakowski, S. (2021). Artificial intelligence and management: The automation-augmentation paradox. The Academy of Management Review, 46(1), 192-210. https://doi.org/10.5465/amr.2018.0072
Schulz, M., & Roßnagel, C. S. (2010). Informal workplace learning: An exploration of age differences in learning competence. Learning and Instruction, 20(5), 383-399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2009.03.003
Shekari, H., & Hosseini, H. (2020). Investigating the Effect of Jihadi Management on Employees Social Undermining with Considering the Mediating Role of Leader Member Exchange in Youth and Sport Office in Yazd Province. Organizational Behavior Management in Sport Studies, 7(25), 137-148. https://fmss.journals.pnu.ac.ir/article_7115.html
Shekari, H., Hosseini, H., & Jalalian, N. (2025). Developing a Model of the Impact of Knowledge Risk Management on Organizational Sustainability Considering the Mediating Role of Employees' Innovative Behavior. Dynamic Management and Business Analysis, 4(3), 278-295. https://www.dmbaj.com/index.php/dmba/article/view/273
Sumantri, O. R., & Saraswati, K. D. H. (2025). AI and Gen Z: Enhancing workplace well-being through informal learning. Tarumanagara International Conference on the Applications of Social Sciences and Humanities, Jakarta, Indonesia.
Tumelo, T. N., & Donald, F. M. (2025). Perceived job insecurity, facades of conformity, emotional exhaustion and disengagement. Sa Journal of Industrial Psychology, 51, 1-9. https://doi.org/10.4102/sajip.v51i0.2221
Valtonen, A., Saunila, M., Ukko, J., Treves, L., & Ritala, P. (2025). AI and employee wellbeing in the workplace: An empirical study. Journal of Business Research, 199, 115584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2025.115584
Wu, N., Liu, S., Yu, S., & Wang, H. (2022). How employees perceive artificial intelligence implementation: A dual-pathway model linking human-AI collaboration climate to employee creativity. Journal of Business Research, 145, 237-246.
Xu, G., Xue, M., & Zhao, J. (2023). The Relationship of Artificial Intelligence Opportunity Perception and Employee Workplace Well-Being: A Moderated Mediation Model. International journal of environmental research and public health, 20(3), 1974. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20031974
Yang, B., Zhao, C., Zhu, Y., & Li, X. (2024). How daily job insecurity links to next-day ingratiation: The roles of emotional exhaustion and power distance orientation. Psychology research and behavior management, 17, 2807-2818. https://doi.org/10.2147/PRBM.S438242
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Hamideh Shekari (Author); Najmeh Jalalian; Mahmood Kamali Zarch, Mohammad Hosein Karimnezhad (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.










