A Comprehensive Model of Factors Influencing Audit Failure: A Logistic Regression Approach
Keywords:
Audit failure, audit error, audit commentAbstract
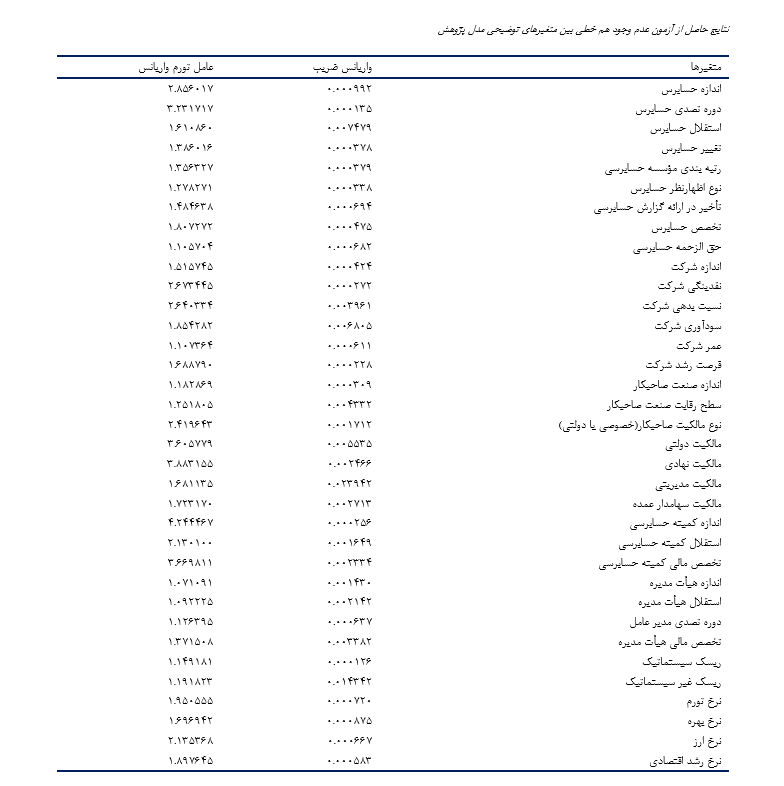
The present study aims to explain the influencing factors—including auditor characteristics, client characteristics, stock market features, and macroeconomic factors—on failure in companies listed on the Tehran Stock Exchange. To achieve this objective, 1,848 firm-year observations (154 companies over 12 years) were collected from the annual financial reports of companies listed on the Tehran Stock Exchange during the period from 2011 to 2022. The study findings indicate that auditor size, auditor tenure, auditor independence, audit firm ranking, type of auditor's opinion, audit report delay, auditor specialization, audit fees, company size, company liquidity, company profitability, institutional ownership, major shareholder ownership, board independence, CEO tenure, inflation rate, exchange rate, and economic growth rate have a negative and significant impact on audit failure. Conversely, auditor change, company's debt ratio, government ownership, unsystematic risk, and interest rate have a positive and significant effect on audit failure. Finally, the results show that, statistically, company age, company growth opportunities, client industry size, client industry competition level, client ownership type (private or public), managerial ownership, audit committee size, audit committee independence, audit committee financial expertise, board size, board financial expertise, and systematic risk do not have a significant effect on audit failure.
Downloads
References
Aggreh, M., Malgwi, C. A., & Enyi-Igbokwe, A. E. (2018). Does Adoption of International Financial Reporting
Standards (IFRS) Affect Financial Performance? Evidence From Nigerian Deposit Money Banks. International
Journal of Accounting and Financial Reporting, 8(3), 51. https://doi.org/10.5296/ijafr.v8i3.13309
Bebbington, J., & Larrinaga, C. (2024). The influence of Power’s audit society in environmental and sustainability
accounting. Qualitative Research in Accounting & Management, 21(1), 21-28. https://doi.org/10.1108/QRAM-01-
-0007
Chang, C., Chi, W., & Liu, C. (2003). Client Characteristics and Auditor Switch in an Audit Failure.
Chu, L., Fogel-Yaari, H., & Zhang, P. (2024). The Estimated Propensity to Issue Going Concern Audit Reports and Audit
Quality. Journal of Accounting, Auditing & Finance, 39(2). https://doi.org/10.1177/0148558X221079011
De Fuentes, C., & Porcuna, R. (2019). Predicting audit failure: evidence from auditing enforcement releases. Spanish
Journal of Finance and Accounting, 48(3), 274-305. https://doi.org/10.1080/02102412.2018.1524220
Francis, J. R. (2011). A framework for understanding and researching audit quality. Auditing: A Journal of Practice &
Theory, 30(2), 125-152. https://doi.org/10.2308/ajpt-50006
Hamidian, M., & Seifi, G. (2022). The Relationship Between Product Diversification and Audit Errors in Tehran Stock
Exchange. Accounting and Management Perspective, 5(69), 100-115.
https://www.jamv.ir/article_163898.html?lang=en
Hassani, M. (2021). Evaluating the Relationships Among the Risk of Undetected Errors Due to Audit Error Probability,
Competitive Market Environment of Audit Services, and Audit Service Pricing. Accounting Knowledge Journal,
(1), 45-68. https://www.sid.ir/paper/399235/en
Hassas Yeganeh, Y., & Azinfar, K. (2010). The Relationship Between Audit Quality and Audit Firm Size. Accounting
and Auditing Reviews(61), 85-98. https://acctgrev.ut.ac.ir/article_21687.html
Hemmati, A., Hejazi, R., & Sedaghat Parast, E. (2020). The Impact of Information Complexity on Audit Failures in
Corporate Fraud (Tehran Stock Exchange). Professional Auditing Research Quarterly, 1(1), 34-55.
Kabir, H., Su, L., & Rahman, A. (2016). Audit failure of New Zealand finance companies-an exploratory investigation.
Pacific Accounting Review, 28(3), 279-305. https://doi.org/10.1108/PAR-10-2015-0043
Muraina, A., Okpara, E., & Ahunanya, S. (2010). Transparency in corporate governance; A comparative study of
ENRON, USA and Cadbury PLC, Nigeria. Medwell Journals, 5(6), 471-476.
https://doi.org/10.3923/sscience.2010.471.476
Osho, A., Olutayo, M. E., & Olayinka, E. A. (2021). International financial reporting standards (IFRS) and financial
performance of multinational companies in Nigeria. The Journal of Accounting and Management, 11(2).
Palmrose, Z. V. (1988). An analysis of auditor litigation and audit service quality. Accounting review, 55-73.
https://www.jstor.org/stable/247679
Xie, F. (2021). Analysis of Measures of Audit Failure. Journal of Forensic and Investigative Accounting, 13(2).
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engfailanal.2021.105550
Yuan, H., Zhang, C., Kong, D., & Shi, H. (2019). The consequence of audit failure on audit firms: evidence from IPO
approval in China. China Journal of Accounting Studies, 7(2), 245-269.
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Journal of Technology in Entrepreneurship and Strategic Management (JTESM)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.










