Designing an Adaptive Model for Analyzing Antecedents and Consequences of Organizational Silence in the Supreme Audit Court: A Case Study of Six Regions
Keywords:
Antecedents and Consequences of Organizational Silence, Organizational Silence, Managers and Deputies of the Supreme Audit CourtAbstract
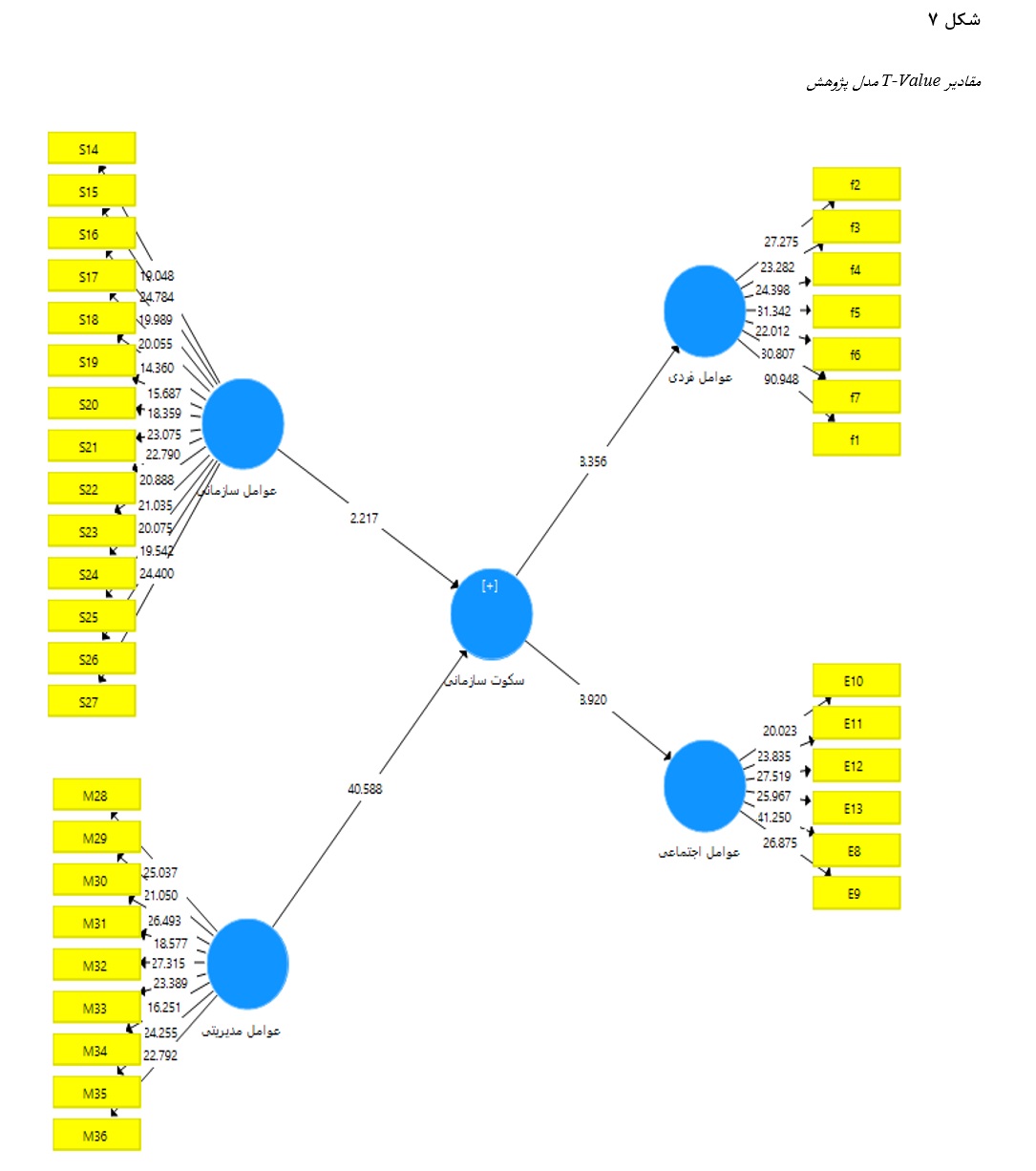
In recent years, due to changes in organizations and their environments, the importance of human resources has increased, bringing attention to the phenomenon of organizational silence. This study aims to design an adaptive model for analyzing the antecedents and consequences of organizational silence in the Supreme Audit Court. The research methodology is applied in terms of its objective and mixed in terms of data collection, with a qualitative phenomenological method in the first part and a quantitative descriptive-survey in the second. In the qualitative phase, semi-structured in-depth interviews were conducted with key informants and experts to identify the antecedents and consequences of organizational silence. Upstream documents and existing written records were analyzed, and the literature was extensively reviewed. Data on components and indicators were collected through interviews until theoretical saturation was reached, after which concepts were extracted, categorized, and interrelationships were identified. A researcher-made questionnaire was then developed based on these findings and tested on the statistical sample. The qualitative sample included managers and deputies of the six regional offices, with 40 individuals purposefully selected, achieving theoretical saturation after interviewing 31. Additionally, national and international scientific documents, books, reports, and articles were reviewed. The quantitative sample consisted of 1,000 employees from the six regional offices, with 278 randomly selected using Cochran's formula. Data analysis in the qualitative phase employed the Stevick-Colaizzi-Keen technique, while SPSS and Smart-PLS software were used for quantitative data analysis. In the qualitative part, 110 key codes were identified for antecedents, condensed into 32 formulated meanings conceptualized into organizational and managerial factors. For consequences, 92 codes were condensed into 34 meanings categorized as individual and social factors. One-way ANOVA results indicated no significant difference in organizational silence among groups. Factor analysis results showed that the measurement scale for all indicators was satisfactory, confirming the measurement tool's quality. Factor loadings, all ≥0.4, indicated acceptable reliability, with construct variance exceeding measurement error variance, ensuring the model's reliability.
Downloads
References
Akan, B. B., & Oran, F. Ç. (2017). Akademisyenlerin Örgütsel Sessizlik Algilari: Konuya Ilişkin Bir Uygulama.
Kırklareli Üniversitesi İktisadi ve İdari Bilimler Fakültesi Dergisi, 6(5), 72-90.
https://dergipark.org.tr/en/pub/klujfeas/issue/32183/349159
Armandei, M., Vaziri, M., & Adli, F. (2016). An investigation of the factors influencing organizational silence from the
perspective of employees. The Journal of New Thoughts on Education, 12(2), 115-144.
https://doi.org/10.22051/jontoe.2016.2393
Arshad, M. A., & Ullah, S. (2023). Culture of Silence in an Organization and How it Effect the Organization and
Employees’ Performance. In.
Bentiba, Z., & Khelil, S. (2022). Organizational silence (Basic concepts and its effects). IJEP, 5(2), : 34-47.
https://www.ijep.dz/index.php/IJEP/article/view/74
Bryant, M., & Wolfram Cox, J. (2004). Conversion stories as shifting narratives of organizational change. Journal of
Organizational Change Management, 17(6), 578-592. https://doi.org/10.1108/09534810410564569
Çakici, Y. d. d. a. (2008). Örgütlerde sessiz kalınan konular sessizliğin nedenleri ve algılanan sonuçları üzerine bir
araştırma. Çukurova Üniversitesi Sosyal Bilimler Enstitüsü Dergisi, 17(1), 117-134.
https://dergipark.org.tr/en/pub/cusosbil/issue/4378/60013
Çakıcı, Y. d. d. a. (2007). Örgütlerde sessizlik: Sessizliğin teorik temelleri ve dinamikleri. Çukurova Üniversitesi Sosyal
Bilimler Enstitüsü Dergisi, 16(1), 145-162. https://dergipark.org.tr/en/pub/cusosbil/issue/4376/59941
Cetin, A. (2020). Organizational silence and organizational commitment: a study of Turkish sport managers. Annals of
Applied Sport Science, 8(2), 0-0.
http://aassjournal.com/browse.php?a_id=830&slc_lang=en&sid=1&printcase=1&hbnr=1&hmb=1
Danaeefard, H., & Panahi, B. (2010). An analysis of employee’s attitudes in public organizations: explanation of
organizational silence climate and silence behavior. Transformation management journal, 2(3), 1-19.
https://doi.org/10.22067/pmt.v2i3.4253
Dyne, L. V., Ang, S., & Botero, I. C. (2003). Conceptualizing Employee Silence and Employee Voice as
Multidimensional Constructs. Journal of Management Studies, 40(6), 1359-1392. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-
00384
Erigüç, G., Özer, Ö., Sonğur, C., & Turaç, İ. S. (2014). Bir devlet hastanesinde hemşirelerde örgütsel sessizlik üzerine
bir araştırma. Çankırı Karatekin Üniversitesi İktisadi ve İdari Bilimler Fakültesi Dergisi, 4(2), 61-84.
https://dergipark.org.tr/en/pub/ckuiibfd/issue/32903/365521
Halis, M., & Ay, D. A. (2017). Kurumsallaşma Düzeyinin Örgütsel Sessizlik Üzerine Etkisi: Bir Araştirma. Cumhuriyet
Üniversitesi İktisadi ve İdari Bilimler Dergisi, 18(2), 43-62. https://dergipark.org.tr/en/download/article-file/383177
Hassani, S., Ahmadi, S. A. A., Sarmast, B., & Alvedari, H. (2020). Designing a Comprehensive Organizational Silence
Model Based on the Five Pillars of the Organization in Selected State Universities in Tehran. Public Organizations
Management, 8(2), 97-112. https://doi.org/10.30473/ipom.2019.48652.3804
Hedin, U.-C., & Månsson, S.-A. (2012). Whistleblowing processes in Swedish public organisations—complaints and
consequences. European Journal of Social Work, 15(2), 151-167. https://doi.org/10.1080/13691457.2010.543890
Jones, A., & Kelly, D. (2014). Deafening silence? Time to reconsider whether organisations are silent or deaf when things
go wrong. BMJ Quality & Safety, 23(9), 709-713. https://qualitysafety.bmj.com/content/23/9/709.short
Küçükeşmen, E., & Çarıkçı, İ. (2018). ÖRGÜTSEL ADALET ALGISI VE ÖRGÜTSEL BAĞLILIĞA ETKİSİ: KAMU
ÇALIŞANLARI ÜZERİNE BİR ARAŞTIRMA. Uluslararası İktisadi ve İdari Bilimler Dergisi, 4(1), 24-44.
https://doi.org/10.29131/uiibd.358527
Milliken, F. J., Morrison, E. W., & Hewlin, P. F. (2003). An Exploratory Study of Employee Silence: Issues that
Employees Don’t Communicate Upward and Why. Journal of Management Studies, 40(6), 1453-1476.
https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-6486.00387
Morrison, E. W., & Milliken, F. J. (2000). Organizational Silence: A Barrier to Change and Development in a Pluralistic
World. The Academy of Management Review, 25(4), 706-725. https://doi.org/10.2307/259200
Nikmaram, S., Yamchi, H. G., Shojaii, S., Zahrani, M. A., & Alvani, S. M. (2012). Study on relationship between
organizational silence and commitment in Iran. World Applied Sciences Journal, 17(10), 1271-1277.
Iran/links/57d6528708ae601b39aa765a/Study-on-Relationship-Between-Organizational-Silence-andCommitment-in-Iran.pdf
Park, C., & Keil, M. (2009). Organizational Silence and Whistle-Blowing on IT Projects: An Integrated Model. Decision
Sciences, 40(4), 901-918. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-5915.2009.00255.x
Pinder, C. C., & Harlos, K. P. (2001). Employee silence: Quiescence and acquiescence as responses to perceived injustice.
In Research in Personnel and Human Resources Management (Vol. 20, pp. 331-369). Emerald Group Publishing
Limited. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0742-7301(01)20007-3
Podsakoff, P. M., MacKenzie, S. B., Paine, J. B., & Bachrach, D. G. (2000). Organizational Citizenship Behaviors: A
Critical Review of the Theoretical and Empirical Literature and Suggestions for Future Research. Journal of
Management, 26(3), 513-563. https://doi.org/10.1177/014920630002600307
Sadeghi, M., & Razavi, M. R. (2020). Organizational silence, organizational commitment and creativity: The case of
directors of Islamic Azad University of Khorasan Razavi. European Review of Applied Psychology, 70(5), 100557.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.erap.2020.100557
Tanhaei, M. H., Nasre Esfahani, A., Nilipour Tabatabaei, S. A., & Akhavan Sarraf, A. R. (2018). Recreation of
antecedents and consequences of employees' organizational silence case study: Isfahan Municipality. Journal of
Applied Sociology, 29(4), 147-166. http://jas.ui.ac.ir/article_22969_en.html
Vakola, M., & Bouradas, D. (2005). Antecedents and consequences of organisational silence: an empirical investigation.
Employee Relations, 27(5), 441-458. https://doi.org/10.1108/01425450510611997
Yıldırım, A., & Çarıkçı, O. (2017). MESLEKİ VE TEKNİK ANADOLU LİSELERİNDE GÖREV YAPAN EĞİTİM
YÖNETİCİSİ VE ÖĞRETMENLERİN ÖRGÜTSEL SESSİZLİK DÜZEYLERİNİN İNCELENMESİ [Anatolian
vocational and technical education high school of teachers and manager investigation of organizational levels of
silence]. Süleyman Demirel Üniversitesi Vizyoner Dergisi, 8(19), 33-43. https://doi.org/10.21076/vizyoner.345090
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Journal of Technology in Entrepreneurship and Strategic Management (JTESM)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.










